Tax Planning and Structuring for UAE Companies
Last Reviewed: 22 August 2025
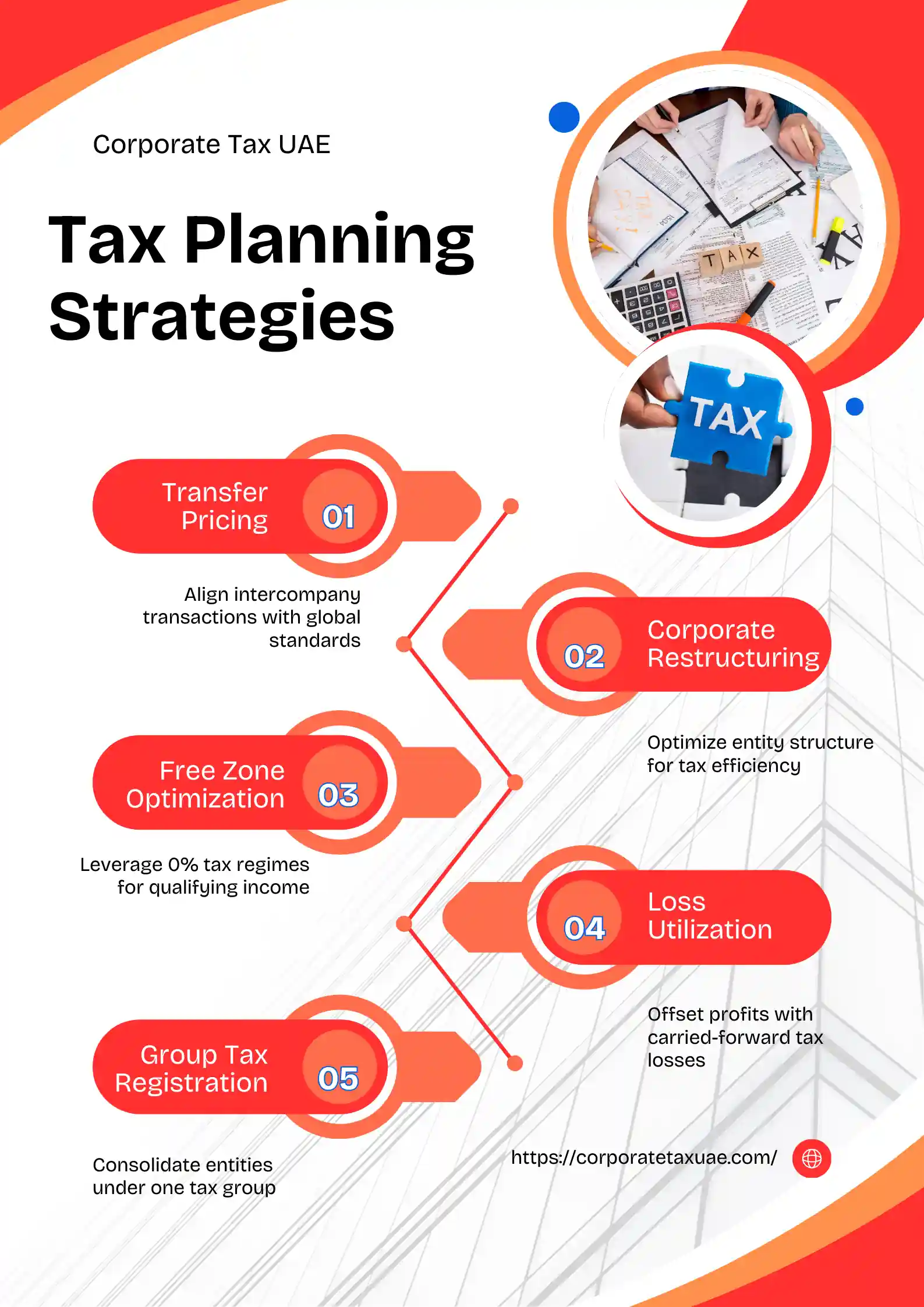
Strategic Tax Planning Approaches for UAE Companies
Assess and Select the Right Legal Structure
- LLC (Limited Liability Company): Standard for mainland operations; subject to full CT on profits exceeding AED 375,000.
- Free Zone Entity (FZC or FZ-LLC): Tax incentives apply if QFZP criteria met; rapid market entry for international ventures.
- Hybrid structures: Combine Free Zone for export/holding activities and mainland for direct domestic trade.
Structure vs. Tax Exposure
| Business Model | Free Zone Qualifying Income | Mainland Income | Expected Tax Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Free Zone (QFZP compliant) | 0% | None | Low |
| Mainland Company | None | 100% | High |
| Hybrid (FZ + Mainland) | Partial | Partial | Medium |
For new and established businesses, regularly reviewing your structure, especially ahead of regulatory changes, can unlock tax savings, investment appeal, and compliance simplicity.

Maximize Free Zone Benefits but Meet All QFZP Criteria
QFZP Requirements Summary:
- Incorporated or registered in a recognized UAE free zone
- Earn qualifying income (see below)
- Maintain adequate substance: assets, employees, OPEX in the free zone
- Prepare and submit audited financial statements
- Pass the de minimis non-qualifying income test (≤ AED 5 million or 5% of total revenue per annum, whichever is lower)
- Comply with transfer pricing and avoid excluded activities
| Category | 0% CT on Qualifying Income? | 9% CT on Non-Qualifying? | Taint Rule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Qualifying Free Zone | Yes (if all criteria met) | Yes (on non-qualifying) | Status lost for 5 years if de minimis breached |
| Non-QFZP Free Zone | No | Yes (all income) | N/A |
Examples of Qualifying Activities
- Trading with other free zone companies
- International trading and exports
- Holding company (shares, securities)
- Ship ownership/operation, reinsurance, headquarter services to group entities, qualifying logistics and distribution
Common Compliance Traps
- Exceeding de minimis non-qualifying income threshold
- Not having real economic substance (for example, virtual office/light staffing)
- Conducting excluded activities (banking, insurance with non-FZ partners, IP exploitation, or property income except in specific FZ/FZ transactions)
Case Study
A Dubai logistics FZCO nearly lost its QFZP status when a major mainland sales contract pushed non-qualifying revenue over the limit. Timely restructuring, redirecting domestic sales via a new mainland branch, helped preserve its free zone 0% rate on export activities.

Leverage Group Structuring, Tax Group, and Reliefs
- Filing a single tax return
- Consolidating profits/losses to offset against each other
- Tax-free intra-group asset and liability transfers
- Simplified administration
However, small business relief thresholds (AED 3 million revenue cap) and the standard AED 375,000 tax-free profit threshold apply to the group as a whole; not per entity. There’s also joint liability for group debts and tax.
| Grouping Type | Ownership Threshold | Consolidated Filing | Loss Offsets | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Group | ≥95% | Yes | Yes | Relief/thresholds apply at group level |
| Qualifying Group | ≥75% | Loss transfers | Yes | Separate returns, looser structure |
This is particularly valuable for larger, multi-entity operating groups, reducing tax on fluctuating results across business lines.

Small Business and SME Tax Planning
SMEs remain the backbone of the UAE’s new economy. The Small Business Relief regime permits eligible businesses (revenue ≤ AED 3 million/year) to:
-
- Elect for simplified tax treatment
- Avoid most corporate tax computation and compliance burdens (but MUST still register and file a simplified annual return)
- Maintain loss carry-forwards and interest expense carry-overs outside the election year
SME Case Calculator Example:
| Metric | Scenario A | Scenario B | Scenario C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue (AED) | 2,500,000 | 2,800,000 | 3,500,000 |
| Eligible for Relief? | Yes | Yes | No |
| Profit (AED) | 100,000 | 750,000 | 1,000,000 |
| CT Payable | 0 | 0 | 56,250 (on 625k over 375k, at 9%) |
Note: Once revenue exceeds AED 3 million in any year up to Dec 2026, full compliance resumes from that period onwards; separating businesses to stay under the cap is penalized by the FTA’s anti-abuse provisions.
- Keep robust records, including bank statements, sales ledgers, invoices, and retain for 7 years.
- Electing for relief eliminates full tax computation but not audit obligations, so accurate bookkeeping remains vital.

Transfer Pricing and Open Market Value
All related-party and connected-person transactions (for example, intra-group services, management fees, royalties, intercompany loans, supply chain cross-charges) must be:
- Priced at arm’s length, i.e., equivalent to what independent parties would pay
- Supported by documentation (master file, local file, transfer pricing report for larger entities)
- Disclosed in the CT return (mandatory TP disclosure form for all; files required if revenue ≥ AED 200m or MNE group revenue ≥ AED 3.15 bn)
Common transfer pricing methods under the law:
- Comparable Uncontrolled Price (CUP)
- Cost Plus
- Resale Price
- Transactional Net Margin (TNMM)
- Profit Split
Failing documentation or mispricing risks substantial penalties, including upward adjustment to taxable income and fines.
Practical Example:
A family group runs logistics in a free zone and manufacturing in the mainland, trading goods between them. Each invoice must be benchmarked in line with market rates, and inter-company agreements must reflect economic reality. Annual master files/local files must justify and evidence all major cross-charges, even in loss years.

Double Taxation Agreements (DTAs): Maximizing Relief on Cross-Border Income
The UAE has signed over 140 DTAs covering all continents, allowing UAE-resident businesses and individuals to:
- Avoid or reduce double taxation for dividends, royalties, interest, and business profits
- Secure lower withholding tax rates on cross-border payments
- Offset foreign tax paid via credits in the UAE (limited to the UAE’s CT payable on that income)
When structuring cross-border investments or group operations, always:
- Ensure the UAE entity’s residency and substance satisfy treaty tests
- Keep a valid Tax Residency Certificate for each applicable year (issued by the FTA)
- Seek treaty relief proactively on source-country payments; recover/offset via UAE returns
For example, a UAE holding company receives dividends from a treaty jurisdiction where tax is withheld. The treaty overrides local laws, so only the reduced treaty WHT applies, and the UAE owner can often claim it as a credit.

Optimise Income and Expense Recognition, Deductions, and Allowances
Strategic management of timing improves your after-tax profits:
- Defer revenue: legally push large receipts into the next tax period, if possible
- Accelerate expenses: bring forward deductible expenses/investments before year-end
- Capital allowances: claim depreciation on fixed assets (machinery, vehicles)
- R&D incentives: new deductions available for research, innovation, and renewables
Pro Tip: Document ALL expenses with contracts, invoices, and payment proofs; loose recordkeeping risks disallowance, audits, and penalties.
Compliance and Reporting: Deadlines, Steps, and Technology
1. Register for Corporate Tax:
- Every business (even those below thresholds or in free zones).
- Apply via EmaraTax portal; obtain CT registration number.
2. Maintain Thorough Records:
- Financial statements (audited if revenue > AED 50m or QFZP).
- Invoices, contracts, payroll, expense reports.
3. Prepare and File Annual Tax Return:
- Due no later than 9 months after financial year-end.
4. Transfer Pricing Disclosure:
- Complete TP form as part of CT filing (even if not mandated for master file/local file).
5. Pay Any Tax Due:
- Via FTA portal before the tax return deadline

Penalties:
- Late registration: AED 10,000
- Late filing: AED 500/month
- Poor records or inaccurate returns: up to AED 50,000
- Repeated non-compliance can cause further FTA scrutiny or audits.
Role of Technology:
Many companies are turning to accounting ERP, e-invoicing, and cloud tax planning software. These reduce manual errors, support compliance, and ensure readiness for audits or FTA reviews.
UAE Tax Planning FAQs
What is the corporate tax rate in the UAE in 2025?
0% on profits up to AED 375,000, 9% above that, 15% for certain large multinationals.
Can free zone companies still pay 0% corporate tax?
Yes, but only on qualifying income and if all QFZP criteria and substance rules are met.
What is Small Business Relief under UAE Corporate Tax?
SMEs with ≤ AED 3 million in revenue per year until end-2026 can elect simplified reporting and pay 0% CT, but must still register and file annual returns.
How does transfer pricing apply in the UAE?
All cross-border and related-party transactions must be priced at arm’s length and documented; large entities must maintain transfer pricing files.
What happens if my free zone company “taints” QFZP status?
Breaching the de minimis limit immediately results in 9% CT on all income for that year and next four years, no QFZP relief.
How do I get DTA relief?
Ensure legal UAE tax residency, apply for an FTA tax residency certificate, and claim foreign tax credits per relevant treaty.
Do I need to file a tax return if my company pays 0% tax?
Yes, registration and filing are mandatory for all entities (mainland, free zone, SME), regardless of tax due.
Secure Your Tax Position and Act Now
The UAE tax landscape offers more opportunity and pitfalls than ever. Proactive, expert-led tax planning is no longer optional: it’s a business imperative for growth, funding, and peace of mind.